Part 10
Azure Backup
Azure Backup is a cloud-based data protection solution provided by Microsoft. It is designed to back up and restore data from the Microsoft Azure cloud, ensuring business continuity in case of data loss or disasters. Azure Backup supports a wide range of scenarios, including on-premises systems, Azure VMs, SQL databases, file shares, and more.
Key Features
- Centralized Backup Management: Manage backups for on-premises and Azure resources from the Azure portal.
- Data Security: Encryption in transit and at rest, with the option to use your own keys.
- Long-Term Retention: Options for long-term data retention to meet regulatory requirements.
- Cost-Effective: Pay-as-you-go model eliminates the need for on-premises backup infrastructure.
- Disaster Recovery Integration: Seamless integration with Azure Site Recovery for disaster recovery.
- Application-Aware Backups: Supports backups for critical workloads like SQL Server, Exchange, and SharePoint.
- Incremental Backups: Saves storage space and reduces bandwidth consumption.
Common Backup Scenarios
Azure Virtual Machines
Back up Azure VMs (Windows and Linux) using the Azure Backup service.On-Premises Servers
Use the Azure Backup Agent or Azure Backup Server to back up files, folders, and applications from on-premises servers.Azure Files
Backup and restore Azure file shares with point-in-time recovery.SQL Server Backups
Backup SQL databases hosted on Azure.
Benefits
- Simplified backup management.
- Scalability to meet growing data needs.
- High availability and reliability.
- Compliance with industry regulations.
For more information, visit the Azure Backup documentation.
What Can Be Backed Up with Azure Backup?
Azure Backup supports a wide variety of backup scenarios for both on-premises and cloud resources. Below is a detailed list of what you can back up:
On-Premises
- Files, Folders, and System State:
Use the Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) agent. - On-Premises VMs (Hyper-V and VMware):
Protect these workloads using Data Protection Manager (DPM) or Azure Backup Server (MABS). - Other On-Premises Workloads:
Back up applications like SQL Server, Exchange, and SharePoint using DPM or MABS.
Azure Virtual Machines
- Entire VMs:
Back up Windows/Linux VMs using Azure Backup extensions. - Files, Folders, and System State:
Use the MARS agent for more granular backup options.
Azure Managed Disks
- Back up Azure Managed Disks directly.
Azure File Shares
- Back up Azure File Shares to a storage account.
SQL Server in Azure VMs
- Back up SQL Server Databases running on Azure Virtual Machines.
SAP HANA Databases in Azure VMs
- Back up SAP HANA Databases running on Azure VMs.
Azure Database for PostgreSQL
- Back up Azure Database for PostgreSQL Servers with retention for up to 10 years.
Azure Blobs
- Operational backups for Azure Blobs provide point-in-time recovery.
Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server
- Back up Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server (currently in preview).
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Back up workloads and configurations in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) clusters.
For more information, visit the Azure Backup documentation.
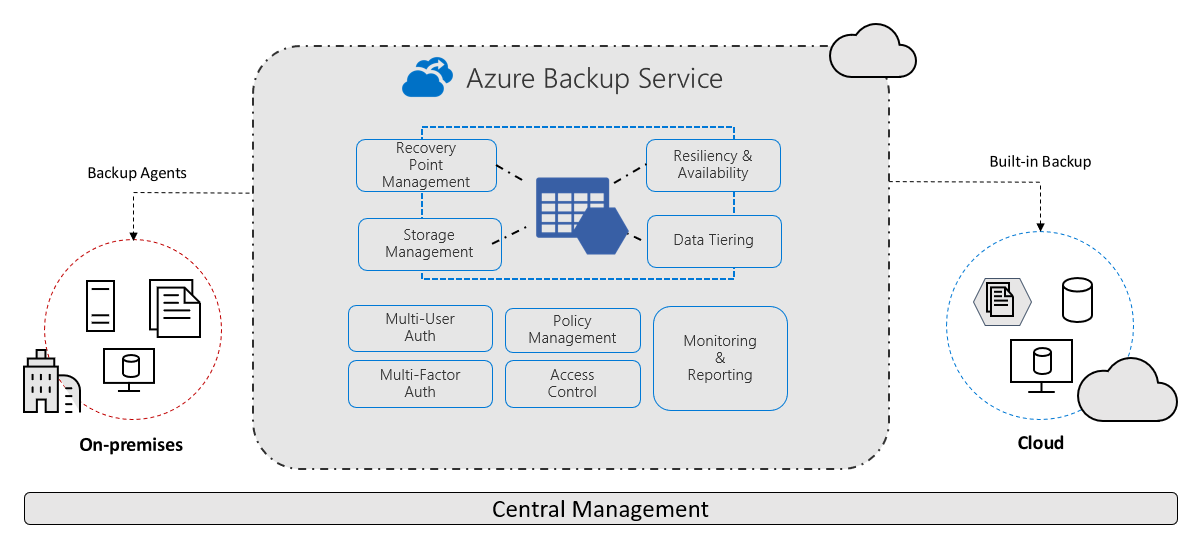

MARS and MABS in Azure Backup
Azure Backup provides different tools for managing on-premises backups, tailored to various use cases. Two commonly used tools are MARS and MABS.
Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) Agent
The MARS agent is designed for simple backup scenarios, specifically for protecting files, folders, and system states on individual machines.
Features of MARS
- Supported Workloads: Files, folders, and system state.
- Backup Target: Azure Recovery Services Vault.
- Supported Systems: Windows Server (various versions) and Windows clients (e.g., Windows 10, 11).
- Granularity: File and folder level backup.
- Usage:
- Ideal for small-scale backup needs or individual servers.
- No dependency on on-premises infrastructure like DPM or MABS.
Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS)
MABS is a more robust solution for larger-scale backup needs. It provides enterprise-grade protection for a variety of on-premises workloads.
Features of MABS
- Supported Workloads:
- Files and folders.
- On-premises VMs (Hyper-V and VMware).
- Application-aware backups for workloads like SQL Server, Exchange, and SharePoint.
- Backup Target:
- Azure Recovery Services Vault for cloud backup.
- Local disk for on-premises backup.
- System Requirements:
- Requires a dedicated Windows Server to run MABS.
- Granularity:
- Application and VM-level protection in addition to file-level backup.
- Usage:
- Suitable for larger environments with diverse workloads.
- Acts as a bridge between on-premises workloads and Azure for backup.
Comparison: MARS vs. MABS
| Feature | MARS | MABS |
|---|---|---|
| Workloads Supported | Files, folders, system state | Files, folders, VMs, applications |
| Backup Target | Azure Recovery Services Vault | Azure Vault + Local Disk |
| Granularity | File-level backup | Application and VM-level backup |
| Ideal Use Case | Individual machines | Enterprise environments |
| Infrastructure Requirements | No dedicated infrastructure | Requires dedicated server |
For more details, visit the Azure Backup documentation.
Recovery Services vault
Restore Options
- Check backed up items
| Restore Option | Details |
|---|---|
| Create a new VM | Quickly creates and gets a basic VM up and running from a restore point.- Specify a name for the VM and select the resource group and virtual network (VNet) in which it will be placed.- The new VM must be created in the same region as the source VM.- If a VM restore fails (e.g., due to unavailable Azure VM SKU), disks are restored in the specified resource group. |
| Restore Disk | Restores a VM disk, which can then be used to create a new VM.- Azure Backup provides a template to help customize and create a VM.- The restore job generates a downloadable template for specifying custom VM settings.- Disks are copied to the specified Resource Group.- Disks can be attached to an existing VM or used to create a new VM via PowerShell.- Useful for customizing or adding new configurations. |
| Replace Existing | Restores a disk to replace a disk on an existing VM.- The current VM must exist.- A snapshot of the VM is taken before replacement and retained in the vault.- Original disks are retained for manual deletion if needed.- Supported for unencrypted managed VMs with linked resources (e.g., managed identities).- Not supported for classic, unmanaged, or generalized VMs. |
| Cross Region Restore | Restores VMs or disks in a secondary (paired) Azure region.- Vault-tier backups are replicated to the secondary region (snapshots are not replicated).- Supports “Create a VM” and “Restore Disks” options.- Not supported for the “Replace Existing” option. |
| Cross Subscription Restore | Restores Azure VMs or disks to a different subscription within the same tenant.- Enabled via the Cross Subscription Restore property in the Recovery Services vault.- Supported only for managed VMs.- Not supported for snapshot-tier recovery points or unmanaged/ADE-encrypted VMs. |
| Cross Zonal Restore | Restores VMs or disks to different Azure zones.- Restores logical zones as per the Azure subscription.- Supported for managed VMs in vaults with Zonal-Redundant Storage (ZRS) or Cross Region Restore (CRR).- Not supported for snapshot-tier restore points or encrypted VMs. |
ASR
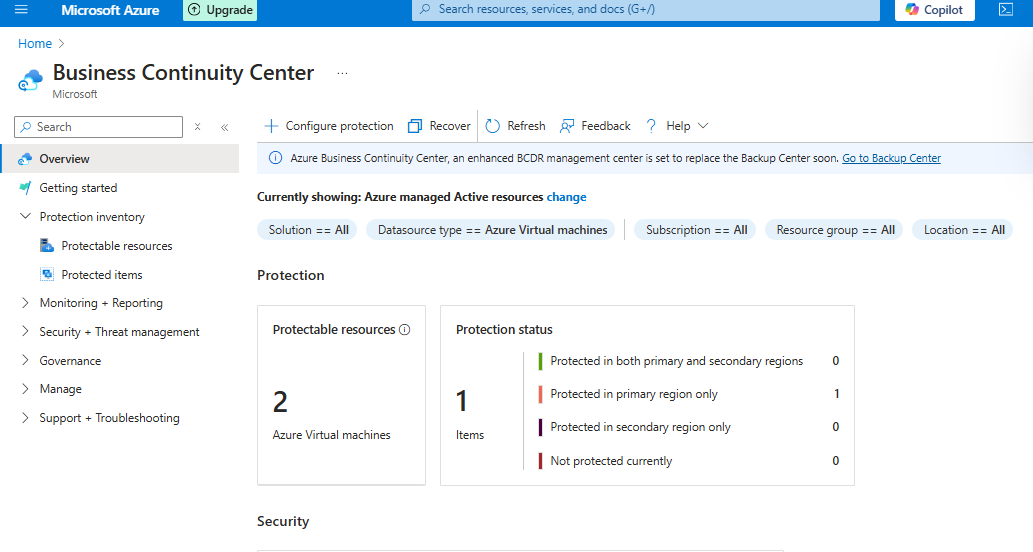
Business Continuity Center
Learning Objectives
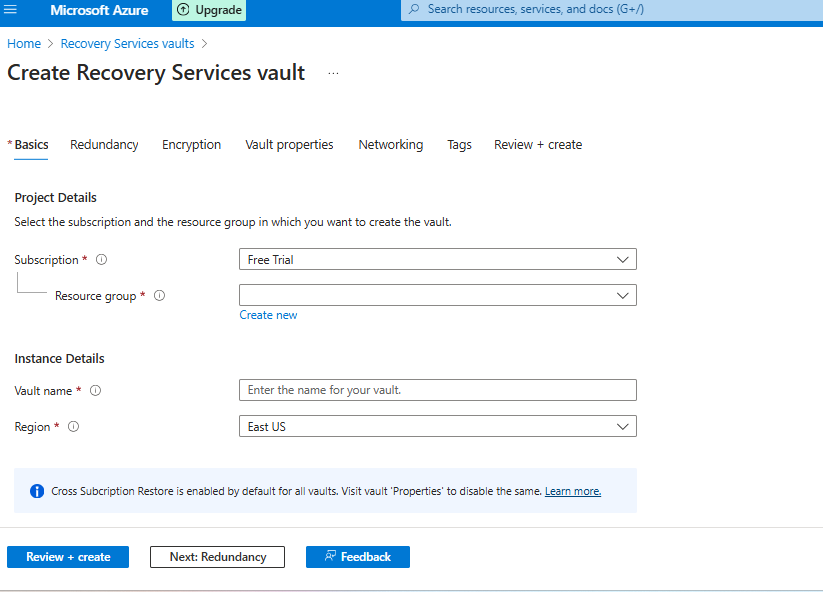
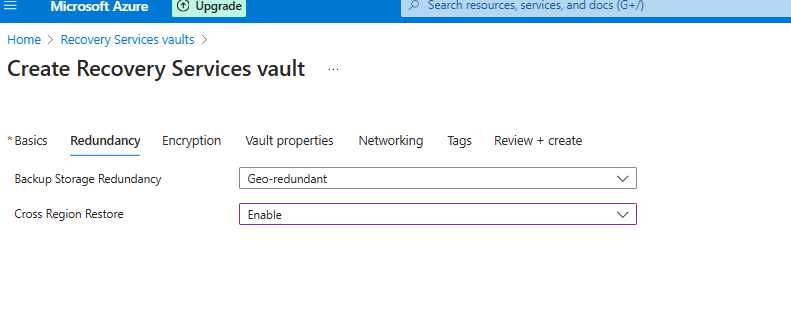
Creating Recovery Service Vault
Learn how to set up a Recovery Services Vault, a foundational step for disaster recovery in Azure.Replicate Azure VM to Secondary Region
Configure Azure VMs to replicate data and services to a secondary region for high availability.Test Failover
Simulate a failover scenario to validate the disaster recovery setup without impacting production.Planned Failover
Execute a planned failover for maintenance or other needs while minimizing disruptions.Failback
Return operations to the primary region after resolving the original issue or completing planned maintenance.